تبدیل نا امن بایت ها(Insecure Deserialization): تفاوت بین نسخهها
از Secure Coding
(صفحهای تازه حاوی «گاهی لازم است برای انتقال برخی داده ها مانند object ها ابتدا اطلاعات را serialize کن...» ایجاد کرد) |
|||
| (۲ نسخهٔ میانیِ همین کاربر نمایش داده نشده است) | |||
| سطر ۳۷۲: | سطر ۳۷۲: | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
| + | === توابع php === | ||
| + | |||
| + | از توابعی می تواند در بروز این آسیب پذیری موثر باشد می توان به | ||
| + | |||
| + | * unserialize | ||
| + | * json_decode | ||
| + | |||
| + | اشاره نمود. | ||
[[category:تبدیل ناامن بایت ها(Deserialization Insecure)]] | [[category:تبدیل ناامن بایت ها(Deserialization Insecure)]] | ||
نسخهٔ کنونی تا ۳۰ مارس ۲۰۲۰، ساعت ۱۰:۵۶
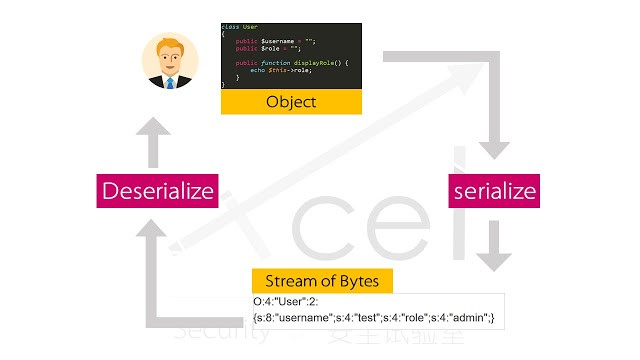
گاهی لازم است برای انتقال برخی داده ها مانند object ها ابتدا اطلاعات را serialize کنید.
به این صورت که داده مورد نظر را به شکل مشخصی قرار می دهیم(serialization) و پس از نتقال آن را به شکل اولیه تبدیل می کنیم(deserialization).
برای مثال در تصویر بالا اطلاعات کاربری شامل username و role و ... ابتدا serialize و انتقال می دهیم و پس از انتقال آن را deserialize می کنیم.
آسیب پذیری insecure deserialization هنگام deserialize شدن داده رخ می دهد و باعث بروز آسیب پذیری های دیگر مانند آسیب پذیری اجرای کد از راه دور می شود.
محتویات
]روش های جلوگیری[ویرایش]
روش های جلوگیری در PHP[ویرایش]
مثال 1)
<?php
class foo {
public $file = "test.txt";
public $data = "text";
function __destruct(){
file_put_contents($this->file, $this->data);
}
}
$file_name = $_GET['session_filename'];
print "Readfile ".$file_name."<br>";
if(!file_exist($file_name)) {
print "No file\n";
} else{
unserialize(file_get_contents($file_name));
}
روش 1)
<?php
class foo {
public $file = "test.txt";
public $data = "text";
function __destruct(){
file_put_contents($this->file, $this->data);
}
}
$file_name = $_GET['session_filename'];
$allowedvalues = array("allow_value_1", "allow_value_2", "allow_value_3");
if(!in_array($file_name, $allowedvalues)){
die("Such a value is not allowed.");
}
print "Readfile ".$file_name."<br>";
if(!file_exist($file_name)) {
print "No file\n";
} else{
unserialize(file_get_contents($file_name));
}
?>
روش های جلوگیری در ASP.NET[ویرایش]
مثال 1)
public void Serialize(SerializationProductModel pro, String filename) {
System.IO.Stream ms = File.OpenWrite(filename);
BinaryFormatter formatter = new BinaryFormatter();
formatter.Serialize(ms, pro);
ms.Flush();
ms.Close();
ms.Dispose();
}
public SerializationProductModel Deserialize(String filename) {
BinaryFormatter formatter = new BinaryFormatter();
FileStream fs = File.Open(filename, FileMode.Open);
SerializationProductModel obj =
(SerializationProductModel) formatter.Deserialize(fs);
fs.Flush();
fs.Close();
fs.Dispose();
return obj;
}
مثال 2)
using System.Web.Script.Serialization;
public class ExampleClass
{
public T Deserialize<T>(string str)
{
JavaScriptSerializer s = new JavaScriptSerializer(new SimpleTypeResolver());
return s.Deserialize<T>(str);
}
}
روش 1)
public class DemoDeserializationBinder: SerializationBinder {
public override Type BindToType(string assemblyName, string typeName) {
List < Tuple < string, Type >> allowedTypes = new List < Tuple < string, Type >> ();
allowedTypes.Add(new Tuple < string, Type > ("RestAPIService.Models.SerializationProductModel",
typeof(SerializationProductModel)));
foreach(Tuple < string, Type > typeTuple in allowedTypes) {
if (typeName == typeTuple.Item1) {
return typeTuple.Item2;
}
}
throw new ArgumentOutOfRangeException("Disallowed type");
}
}
public SerializationProductModel Secure_Deserialize(String filename) {
//Format the object as Binary
//add Binder
BinaryFormatter formatter = new BinaryFormatter {
Binder = new DemoDeserializationBinder()
};
//Reading the file from the server
FileStream fs = File.Open(filename, FileMode.Open);
SerializationProductModel obj =
(SerializationProductModel) formatter.Deserialize(fs);
//SerializationProductModel pro = (SerializationProductModel)obj;
fs.Flush();
fs.Close();
fs.Dispose();
return obj;
}
روش 2)
using System.Web.Script.Serialization;
public class ExampleClass
{
public T Deserialize<T>(string str)
{
JavaScriptSerializer s = new JavaScriptSerializer();
return s.Deserialize<T>(str);
}
}
روش های جلوگیری در JAVA[ویرایش]
مثال 1)
class Utils
{
// Function to serialize an object and write it to a file
public static void SerializeToFile(Object obj, String filename)
{
try
{
FileOutputStream file = new FileOutputStream(filename);
ObjectOutputStream out = new ObjectOutputStream(file);
// Serialization of the object to file
System.out.println("Serializing " + obj.toString() + " to " + filename);
out.writeObject(obj);
out.close();
file.close();
}
catch(Exception e)
{
System.out.println("Exception: " + e.toString());
}
}
// Function to deserialize an object from a file
public static Object DeserializeFromFile(String filename)
{
Object obj = new Object();
try
{
FileInputStream file = new FileInputStream(filename);
ObjectInputStream in = new ObjectInputStream(file);
// Deserialization of the object to file
System.out.println("Deserializing from " + filename);
obj = in.readObject();
in.close();
file.close();
}
catch(Exception e)
{
System.out.println("Exception: " + e.toString());
}
return obj;
}
}
روش 1)
package com.suducode.safe.deserialization;
import java.io.FilterInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.io.ObjectInputStream;
import java.io.ObjectStreamClass;
import java.util.List;
/**
* This class helps with safely de serializing an object from a stream avoiding the known
* vulnerability in native java de serialization.
*
* @param <T> De-serialized object will be cast to this type.
* @author Sudharshan Krishnamurthy
* @version 1.0
*/
public class SafeDeserializer<T> {
private long length = 0;
private long maxBytes = 0;
private long maxObjects = 0;
private InputStream inputStream;
private List<Class<?>> safeClasses;
/**
* A de-serializer to replace the unsafe ObjectInputStream.readObject() method built into Java. This method
* checks to be sure the classes referenced are safe, the number of objects is limited to something sane,
* and the number of bytes is limited to a reasonable number. The returned Object is also cast to the
* specified type.
*
* @param safeClasses List of Classes allowed in serialized object being read.
* @param maxObjects long representing the maximum number of objects allowed inside the serialized
* object being read.
* @param maxBytes long representing the maximum number of bytes allowed to be read from the InputStream.
* @param inputStream InputStream containing an untrusted serialized object.
* @return Object read from the stream. (cast to the Class of the type parameter)
* @throws IOException might be thrown while reading fom the stream.
* @throws ClassNotFoundException might be thrown while casting the deserialized object.
*/
public SafeDeserializer(List<Class<?>> safeClasses, long maxObjects, long maxBytes, InputStream inputStream) {
this.safeClasses = safeClasses;
this.maxBytes = maxBytes;
this.maxObjects = maxObjects;
this.inputStream = inputStream;
}
public T safelyReadObject() throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
// create an input stream limited to a certain number of bytes
InputStream lis = new SecureFilterInputStream(inputStream);
// create an object input stream that checks classes and limits the number of objects to read
ObjectInputStream ois = new SecureObjectInputStream(lis);
// use the protected ObjectInputStream to read object safely and cast to T
return (T) ois.readObject();
}
/**
* Filter Input stream override to enforce some security rules.
*/
private class SecureFilterInputStream extends FilterInputStream {
protected SecureFilterInputStream(InputStream in) {
super(in);
}
@Override
public int read() throws IOException {
int val = super.read();
if (val != -1) {
length++;
checkLength();
}
return val;
}
@Override
public int read(byte[] bytes, int off, int len) throws IOException {
int val = super.read(bytes, off, len);
if (val > 0) {
length += val;
checkLength();
}
return val;
}
private void checkLength() throws IOException {
if (length > maxBytes) {
throw new SecurityException("Security violation: attempt to deserialize too many bytes"
+ " from stream. Limit is " + maxBytes);
}
}
}
/**
* Object Input stream override to enforce some security rules.
*/
private class SecureObjectInputStream extends ObjectInputStream {
private int objCount = 0;
boolean status = enableResolveObject(true);
protected SecureObjectInputStream(InputStream filteredInputStream) throws IOException {
super(filteredInputStream);
}
@Override
protected Object resolveObject(Object obj) throws IOException {
if (objCount++ > maxObjects) {
throw new SecurityException("Security violation: attempt to deserialize too many objects"
+ " from stream. Limit is " + maxObjects);
}
return super.resolveObject(obj);
}
@Override
protected Class<?> resolveClass(ObjectStreamClass osc) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
Class<?> clazz = super.resolveClass(osc);
if (clazz.isArray() || clazz.equals(String.class)
|| Number.class.isAssignableFrom(clazz) || safeClasses.contains(clazz)) {
return clazz;
}
throw new SecurityException("Security violation: attempt to deserialize unauthorized " + clazz);
}
}
}
توابع php[ویرایش]
از توابعی می تواند در بروز این آسیب پذیری موثر باشد می توان به
- unserialize
- json_decode
اشاره نمود.