تبدیل نا امن بایت ها(Insecure Deserialization)
از Secure Coding
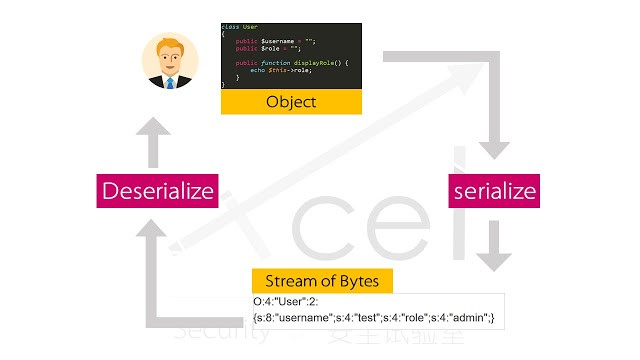
گاهی لازم است برای انتقال برخی داده ها مانند object ها ابتدا اطلاعات را serialize کنید.
به این صورت که داده مورد نظر را به شکل مشخصی قرار می دهیم(serialization) و پس از نتقال آن را به شکل اولیه تبدیل می کنیم(deserialization).
برای مثال در تصویر بالا اطلاعات کاربری شامل username و role و ... ابتدا serialize و انتقال می دهیم و پس از انتقال آن را deserialize می کنیم.
آسیب پذیری insecure deserialization هنگام deserialize شدن داده رخ می دهد و باعث بروز آسیب پذیری های دیگر مانند آسیب پذیری اجرای کد از راه دور می شود.
محتویات
]روش های جلوگیری
روش های جلوگیری در PHP
مثال 1)
<?php
class foo {
public $file = "test.txt";
public $data = "text";
function __destruct(){
file_put_contents($this->file, $this->data);
}
}
$file_name = $_GET['session_filename'];
print "Readfile ".$file_name."<br>";
if(!file_exist($file_name)) {
print "No file\n";
} else{
unserialize(file_get_contents($file_name));
}
روش 1)
<?php
class foo {
public $file = "test.txt";
public $data = "text";
function __destruct(){
file_put_contents($this->file, $this->data);
}
}
$file_name = $_GET['session_filename'];
$allowedvalues = array("allow_value_1", "allow_value_2", "allow_value_3");
if(!in_array($file_name, $allowedvalues)){
die("Such a value is not allowed.");
}
print "Readfile ".$file_name."<br>";
if(!file_exist($file_name)) {
print "No file\n";
} else{
unserialize(file_get_contents($file_name));
}
?>
روش های جلوگیری در ASP.NET
مثال 1)
public void Serialize(SerializationProductModel pro, String filename) {
System.IO.Stream ms = File.OpenWrite(filename);
BinaryFormatter formatter = new BinaryFormatter();
formatter.Serialize(ms, pro);
ms.Flush();
ms.Close();
ms.Dispose();
}
public SerializationProductModel Deserialize(String filename) {
BinaryFormatter formatter = new BinaryFormatter();
FileStream fs = File.Open(filename, FileMode.Open);
SerializationProductModel obj =
(SerializationProductModel) formatter.Deserialize(fs);
fs.Flush();
fs.Close();
fs.Dispose();
return obj;
}
مثال 2)
using System.Web.Script.Serialization;
public class ExampleClass
{
public T Deserialize<T>(string str)
{
JavaScriptSerializer s = new JavaScriptSerializer(new SimpleTypeResolver());
return s.Deserialize<T>(str);
}
}
روش 1)
public class DemoDeserializationBinder: SerializationBinder {
public override Type BindToType(string assemblyName, string typeName) {
List < Tuple < string, Type >> allowedTypes = new List < Tuple < string, Type >> ();
allowedTypes.Add(new Tuple < string, Type > ("RestAPIService.Models.SerializationProductModel",
typeof(SerializationProductModel)));
foreach(Tuple < string, Type > typeTuple in allowedTypes) {
if (typeName == typeTuple.Item1) {
return typeTuple.Item2;
}
}
throw new ArgumentOutOfRangeException("Disallowed type");
}
}
public SerializationProductModel Secure_Deserialize(String filename) {
//Format the object as Binary
//add Binder
BinaryFormatter formatter = new BinaryFormatter {
Binder = new DemoDeserializationBinder()
};
//Reading the file from the server
FileStream fs = File.Open(filename, FileMode.Open);
SerializationProductModel obj =
(SerializationProductModel) formatter.Deserialize(fs);
//SerializationProductModel pro = (SerializationProductModel)obj;
fs.Flush();
fs.Close();
fs.Dispose();
return obj;
}
روش 2)
using System.Web.Script.Serialization;
public class ExampleClass
{
public T Deserialize<T>(string str)
{
JavaScriptSerializer s = new JavaScriptSerializer();
return s.Deserialize<T>(str);
}
}
روش های جلوگیری در JAVA
مثال 1)
class Utils
{
// Function to serialize an object and write it to a file
public static void SerializeToFile(Object obj, String filename)
{
try
{
FileOutputStream file = new FileOutputStream(filename);
ObjectOutputStream out = new ObjectOutputStream(file);
// Serialization of the object to file
System.out.println("Serializing " + obj.toString() + " to " + filename);
out.writeObject(obj);
out.close();
file.close();
}
catch(Exception e)
{
System.out.println("Exception: " + e.toString());
}
}
// Function to deserialize an object from a file
public static Object DeserializeFromFile(String filename)
{
Object obj = new Object();
try
{
FileInputStream file = new FileInputStream(filename);
ObjectInputStream in = new ObjectInputStream(file);
// Deserialization of the object to file
System.out.println("Deserializing from " + filename);
obj = in.readObject();
in.close();
file.close();
}
catch(Exception e)
{
System.out.println("Exception: " + e.toString());
}
return obj;
}
}
روش 1)
package com.suducode.safe.deserialization;
import java.io.FilterInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.io.ObjectInputStream;
import java.io.ObjectStreamClass;
import java.util.List;
/**
* This class helps with safely de serializing an object from a stream avoiding the known
* vulnerability in native java de serialization.
*
* @param <T> De-serialized object will be cast to this type.
* @author Sudharshan Krishnamurthy
* @version 1.0
*/
public class SafeDeserializer<T> {
private long length = 0;
private long maxBytes = 0;
private long maxObjects = 0;
private InputStream inputStream;
private List<Class<?>> safeClasses;
/**
* A de-serializer to replace the unsafe ObjectInputStream.readObject() method built into Java. This method
* checks to be sure the classes referenced are safe, the number of objects is limited to something sane,
* and the number of bytes is limited to a reasonable number. The returned Object is also cast to the
* specified type.
*
* @param safeClasses List of Classes allowed in serialized object being read.
* @param maxObjects long representing the maximum number of objects allowed inside the serialized
* object being read.
* @param maxBytes long representing the maximum number of bytes allowed to be read from the InputStream.
* @param inputStream InputStream containing an untrusted serialized object.
* @return Object read from the stream. (cast to the Class of the type parameter)
* @throws IOException might be thrown while reading fom the stream.
* @throws ClassNotFoundException might be thrown while casting the deserialized object.
*/
public SafeDeserializer(List<Class<?>> safeClasses, long maxObjects, long maxBytes, InputStream inputStream) {
this.safeClasses = safeClasses;
this.maxBytes = maxBytes;
this.maxObjects = maxObjects;
this.inputStream = inputStream;
}
public T safelyReadObject() throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
// create an input stream limited to a certain number of bytes
InputStream lis = new SecureFilterInputStream(inputStream);
// create an object input stream that checks classes and limits the number of objects to read
ObjectInputStream ois = new SecureObjectInputStream(lis);
// use the protected ObjectInputStream to read object safely and cast to T
return (T) ois.readObject();
}
/**
* Filter Input stream override to enforce some security rules.
*/
private class SecureFilterInputStream extends FilterInputStream {
protected SecureFilterInputStream(InputStream in) {
super(in);
}
@Override
public int read() throws IOException {
int val = super.read();
if (val != -1) {
length++;
checkLength();
}
return val;
}
@Override
public int read(byte[] bytes, int off, int len) throws IOException {
int val = super.read(bytes, off, len);
if (val > 0) {
length += val;
checkLength();
}
return val;
}
private void checkLength() throws IOException {
if (length > maxBytes) {
throw new SecurityException("Security violation: attempt to deserialize too many bytes"
+ " from stream. Limit is " + maxBytes);
}
}
}
/**
* Object Input stream override to enforce some security rules.
*/
private class SecureObjectInputStream extends ObjectInputStream {
private int objCount = 0;
boolean status = enableResolveObject(true);
protected SecureObjectInputStream(InputStream filteredInputStream) throws IOException {
super(filteredInputStream);
}
@Override
protected Object resolveObject(Object obj) throws IOException {
if (objCount++ > maxObjects) {
throw new SecurityException("Security violation: attempt to deserialize too many objects"
+ " from stream. Limit is " + maxObjects);
}
return super.resolveObject(obj);
}
@Override
protected Class<?> resolveClass(ObjectStreamClass osc) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
Class<?> clazz = super.resolveClass(osc);
if (clazz.isArray() || clazz.equals(String.class)
|| Number.class.isAssignableFrom(clazz) || safeClasses.contains(clazz)) {
return clazz;
}
throw new SecurityException("Security violation: attempt to deserialize unauthorized " + clazz);
}
}
}
توابع php
از توابعی می تواند در بروز این آسیب پذیری موثر باشد می توان به
- unserialize
- json_decode
اشاره نمود.